1. Fill in the blanks using the correct option given in the bracket:
(i) Employment in the service sector …………. increased to the same extent as
production, (has/has not)
(ii) Workers in
the sector do ……………… not produce goods, (territary/agricultural)
(iii) Most of the workers in the …………….. sector enjoy job security.
(organised/unorganised)
(iv) A ……………..
proportion of labourers in India are working in the unorganised sector,
(large/small).
(v) Cotton is a …………….
product, and cloth is a …………… product, (natural/manufactured)
(vi) The activities in primary. Secondary and territary sectors are ……………
(independent/interdependent)
Answer:
(i) has
(ii) territary
(iii) organised
(iv) large
(v) natural manufactured
(vi)
interdependent.
2. Choose the most correct answer.
(a) The
sectors are classified into public and private sector on the basis of:
(i) employment conditions
(ii) the nature
of economic activity
(iii) Ownership of
enterprises
(iv) number of workers employed
in the enterprise
Answer:
(iii) Ownership of enterprises.
(b) Production of a commodity, mostly through the natural by sector. Process,
is an activity in …………… sector.
(i)
primary
(ii) secondary
(iii) Territary
(iv) Information
technology
Answer:
Primary.
(c) GDP is the sum total of the value of produced goods during a particular
year.
(i) all goods and services
(ii) all final goods and services
(iii)
all intermediate goods and services
(iv) all
intermediate and final goods and services
Answer:
All final goods and services.
(d) In terms of GDP the share of territary sector in 2003 is
(i) between 20 per cent to 30 per cent
(ii) between 30 per cent to 40 per cent
(iii) between 50 per cent to 60 per cent
(iv) 70 per cent.
Answer:
Between 50 per cent to 60 per cent.
3. Match the following:
Problems faced by farming sector Some
possible measures
| 1. Unirrigated land | (a) Setting up agro-based mills |
| 2. Fluctuations in income | (b) Cooperative marketing societies |
| 3. Debt burden | (c) Procurement of food grains by government |
| 4. No job in the off season | (d) Construction of canals by the government |
| 5. Compelled to sell their grains to the local traders soon after harvest. | (e) Banks to provide credit with low interest |
Answer:
| 1. Unirrigated land | (d) Construction of canals by the government |
| 2. Fluctuations in income | (e) Banks to provide credit with low interest |
| 3. Debt burden | (b) Cooperative marketing societies |
| 4. No job in the off season | (a) Setting up agro-based mills |
| 5. Compelled to sell their grains to the local traders soon after harvest. | (c) Procurement of food grains by government |
Question 1.
Find the odd one out and say
why.
(i) Tourist guide, dhobi, tailor,
potter
(ii) Teacher, doctor, vegetable
vendor, lawyer
(iii) Postman, cobbler,
soldier, police constable
(iv) MTNL, Indian
Railways, Air India, SAHARA Airliney All India Radio.
Answer:
(i), (ii), (iii) potter, vegetable
vendor, cobbler, are those who only manage their living; (iv) Sahara Airlines
is in private sector whereas all others are in public sector.
Question 2.
A research scholar looked at the
working people in the city of Surat and found the following: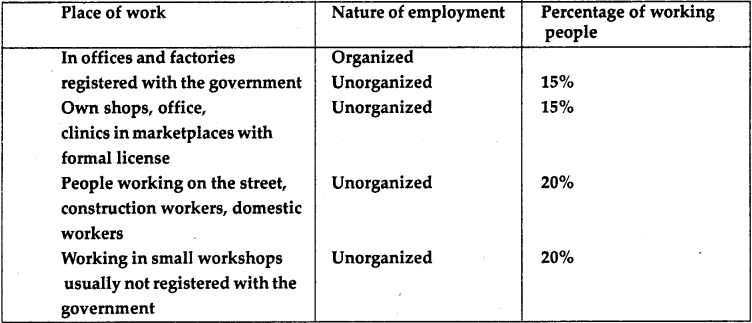
Complete the table. What is the
percentage of workers in the unorganised sector in this city?
Answer:
The proportion of workers in the
unorganised sector in the city of Surat is more than half of the total 15%
number of workers. In organised sector, total % is 15%.
Question 3.
Do you think that the
classification of economic activities into primary, secondary, and territary
is useful? Explain how?
Answer:
The classification of economic activities into primary, Secondary and
territary is useful. It is useful because it relates to our activities which
we do (i) on nature, (ii) through our labour, and (iii) on our expertise
knowledge. Their classification indicates the level of our development.
Question 4.
For each of the sectors that we
came across in this chapter why should the focus on employment and GDP? Could
there be other issues which should be examined? Discuss.
Answer:
Each of the sectors explain its.
Contribution to GDP. Each of the sectors absorbs human resources as well which
shows as to how much each sector generates employment. GDP indicate our level
of development and employment helps give jobs. Literacy and lifespan can also
be examined.
Question 5.
Make a long list of all kinds,
of work that you find adults around you doing for a living. In what way can
you Classify them? Explain your choice.
Answer:
We find people, particularly
adults, doing numerous jobs. There is ‘A’ who tills the land; ‘B’ catching
fishes; C’ weaving charkha and making cloth; “D manufacturing gur from sugar
cane; E taking milk from his village to the city on bicycle; F teaching kids
in the school. A and B are engaged in primary activities; ‘B and ‘C, in
secondary activities; while E and F’ are doing territary activities. The first
two are in the agriculture sector; the second two are in the industrial sector
whereas the third two are engaged in service sector.
Question 6.
How is the territary sector
different from other sectors? Illustrate with a few examples.
Answer:
The territary sector is different
from the primary and secondary sectors in that it supports the other two
sectors. The Territary sector does not produce whereas the other two sectors
Produce goods.
Question 7.
What do you understand by
disguised unemployment? Explain with an example each from the urban and rural
areas.
Answer:
Disguised unemployment is a situation where more people are engaged in an
activity than the required ones. Such People appear to be employed, but they
are not actually employed Such people may not be needed because, without them,
the activity is being done. It is also hidden unemployment.
Question 8.
Distinguish between open
unemployment and distingused unemployment.
Answer:
Open unemployment is one where
there are people w Do not have any job; disguised unemployment is one where
people are engaged and that if some of them withdraw themselves the work will
not suffer. The open unemployment is open as the disguised unemployment is
hidden one. In open unemployment, there is no job at all; a person is
unemployed; Whereas, in disguised unemployment, there is a job and that a
person appears to be employed, but actually, without him, the job does not
suffer.
Question 9.
“Territary sector is not playing
any significant role in the development of Indian economy”. Do you agree? Give
reasons in support of your answer.
Answer:
Territary sector is an important
sector. It plays a very important role in the development of the economy. It
creates numerous jobs; it creates numerous economic activities and
Institutions : banking, trade, commerce, import, and export. The more this
sector is employed, the economy of the country indicates a higher level of
development.
Question 10.
Service sector in India employs
two different kinds of people. Who are these?
Answer:
One type of people are highly
skilled and educated workers. The other type of people are ordinary workers.
The first type of people are limited in number, the other, very large number.
Question 11.
Workers are exploited in the
unorganised sector. Do You agree with this view? Give reasons in support of
your answer.
Answer:
Workers are exploited in the unorganised sector. There are rules in this
sector, but they are not followed; there are jobs in this sector, but they are
low-paid and often not regular. There is no provision for overtime, no leave,
no holiday. There is all work and all exploitation.
Question 12.
How are the activities in the
economy classified on the basis of employment conditions?
Answer:
As regards the employment
conditions, economy is usually Classified into organised and unorganised
sectors. Organised economy is one where the workers enjoy regular employment
conditions. Unorganised sector is one where employment Conditions are
insecure.
Question 13.
Compare the employment
conditions prevailing in the organised and unorganised sectors.
Answer:
Employment conditions in the
organised and unorganised after dastically. In the organised sector, there are
rules and regulations which are followed: there are the laws governing the
employees and the employers in this sector; employment is secure; social
security measures are assured: health facilities are provided. But in the
unorganised, no such facilities are given: no assured employment; no leave and
no holiday. Workers are exploited in the unorganised sector.
Question 14.
Explain the objective of
implementing the NREGA 2005.
Answer:
The objectives of the implementation of the National Rural Employment
Guarantee Act (NREGA), 2005 is to guarantee 100 days of employment in a year
by the government. This is a type of right to work to the rural people who are
able and are in need of a work. In case, the government is unable to provide
work, it gives unemployment allowance.
Question 15.
Using examples from your area,
compare and contrast the activities and functions of private and public
sectors.
Answer:
Public sector is one where the government owns most of the assets of an
enterprise and it is the government which provides all services relating to
that enterprise. Private sector is one where all this is done by the private
individuals or private companies. Railways, post-offices, public health
services are activities which come under public sector.
Reliance Industries Limited (RIL) is a private sector company, privately owned and its services are provided by the company itself.
Question 16.
Discuss and fill the following
table giving one example each from your area.
| Well managed organisation | Badly managed organisation | |
|
Public sector Private sector |
Answer:
Some public sector enterprises do
well while others do not do so for want of adequate funds. Likewise, some
private sector enterprises do well while others seek only profit.
Question 17.
Give a few examples of public
sector activities and explain why the government has taken them up.
Answer:
There are certain public sectors
which the government alone can do. Railway service is so huge a service, so
are activities such as the construction of bridge and harbours and dams. Such
activities involve huge amount of money and infrastructure. These activities
can be done only by the government. No private company can do it, if it does,
it mismanages such activities.
Question 18.
Explain how public sector
contributes to the economic development of a nation.
Answer:
Public sector contributes a lot to
the economic development of a nation. Some of the activities in the public
sector are so important that the government alone can do it. Import and export
activities can be done only under the supervision of the government earns
foreign exchange. It is the government which provides health services, though
at a cost. But such activities are essential for the health of the economy of
a nation.
Question 19.
The workers in the unorganized
sector need protection on the following issues: wages, safety and health.
Explain with examples.
Answer:
As the workers are usually exploited in the organized sector, it is
important that the rules and regulations with regard to their wages, safety
and health should not only be provided, but should be followed strictly.
Question 20.
A study in ahemdabad found that
of 15,00,000 workers in the city, 11,00,000 worked in the organized sector.
The total income of the city in this year (1997-1998) was? 60,000 million. out
of this ? 32,000 million was generated in the organized sector. Present this
data as a table. What kind of the organized sector. Present this data as
table. What kind of should be thought of for generating more employment in the
city?
Answer:
The data with regard to the city of the Ahemdabad relating to the workers
and the income can be stated in the form of a table :
The area for the organized sector can be
enlarged by providing more services , leading thus to more employment.
Question 21.
The following table gives the
GDP in rupees (crores) by the three sectors:
(i) Calculate the share of the three
sectors in GDP for 1950 and 2000.
(ii) Show
the data as a bar diagram similar to Graph 2 in the chapter.
(iii) What conclusion can we draw from the bar graph?
Answer:
(1) Share of GDP for 1500?
1,38,000 crore
(2) Share of GDP for 2000:?
11,49,000 crore. Students may do if themselves, with the help their
teachers.
(3) Though there is increase of
GDP in every sector, but it is the most in the’secondary and territary sectors
it is about 4 time in the primary’ sector; more than 14 times in the secondary
sector; around the sometimes in the territary sector.