Question 1.
Why should magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Answer.
Magnesium is a reactive metal. When it is
exposed to atmosphere for longer time, the oxygen present in the atmosphere
combines and MgO is formed on the metal surface. This oxide layer does not
burn in the flame so magnesium ribbon has to be cleaned with sandpaper before
burning in air.
Question 2.
Write the balanced equations for the
following chemical reactions:
(a) Hydrogen
+ Chlorine ➝ Hydrogen chloride
(b) Barium
chloride + Aluminium sulphate ➝ Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
(c) Sodium +
Water ➝ Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Answer.
The balanced equations are written as:
(a) H
2 + Cl
2 ➝ 2HCl
(b) 3BaCl
2 + Al
2(SO
4)
3 ➝ 3BaSO
4 + 2AlCl
3
(c) 2Na + 2H
2O ➝ 2NaOH + H2
Question 3.
Write the balanced equations with state
symbols for the following reactions:
(a) Solutions
of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble barium
sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride.
(b) Sodium
hydroxide solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in
water) to produce sodium chloride and water.
Answer.
The symbol equations in balanced form for
the reactions are:
(a) BaCl
2(aq) + Na
2SO
4(aq) ➝ BaS0
4(s)+ 2NaCl(aq)
(b) NaOH(aq)
+ HCl(aq) ➝ NaCl(aq) + H
2O(l)
Question 4.
A solution of the substance ‘X’ is used for
white washing.
(a) Name the
substance ‘X’ and write its formula.
(b) Write the
reaction of the substance ‘X’ with water.
Answer.
(a) The
substance ‘X’ is calcium oxide (also called quick lime). Its formula is CaO.
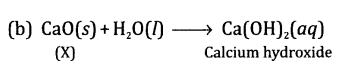
Question 5.
Why is the amount of gas collected in one
of the test tubes in Activity 7 double of the amount collected in the other?
Name the gas.
Answer.
It is so because in water, the hydrogen is
two times more than oxygen by mass and volume. The equation is expressed as:
![]()
Here the two gases have volume in ratio of
2 : 1. The gas is hydrogen.
Question 6.
When you mix solutions of lead(II) nitrate
and potassium iodide.
(a) What is
the colour of the precipitate formed? Name the compound involved.
(b) Write a
balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
(c) What type
of a reaction is this?
Answer.
(a) The
precipitate is yellow in colour. The compound is lead(II) iodide with chemical
formula PbI
2.
(b) Pb(NO
3)
2(aq) + 2KI(aq) ➝ Pbl
2(s) + 2KNO
3(aq)
(c) It is a
double displacement reaction.
Question 7.
Why does the colour of copper sulphate
change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Answer.
Iron nail acquires a brown coating of
copper as a result of displacement reaction. The solution becomes light green.

Question 8.
Give one example of the double displacement
reaction.
Answer.
![]()
Question 9.
Identify the substances that are oxidised
and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions:
(a) 4Na(s) +
O
2(g) ➝ 2Na
2O(s)
(b) CuO(s) +
H
2(g) ➝ Cu(s) + H
2O(l)
Answer.
(a) In this
reaction, sodium (Na) is oxidised to sodium oxide (Na
2O). This means that oxygen (O
2) gets reduced.
(b) In this
reaction, hydrogen (H
2) is oxidised to form water (H
2O) while copper(II) oxide (CuO) is reduced to copper (Cu).
Question 10.
Magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling
flame in air (or oxygen) and changes to a white substance magnesium oxide. Is
magnesium being oxidised or reduced in this reaction?
Answer.
The balanced chemical equation is:
2Mg(s) + O
2(g) ➝ 2MgO(s)
Yes, magnesium (Mg) gets
oxidised to form magnesium oxide (MgO) in this reaction.
is same as the total mass of products. It implies mass can neither be created nor be destroyed during a chemical reaction.
Chapter End Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following statements about the
reaction given below are incorrect?
2PbO(s)
+ C(s) ➝ 2Pb(s) + CO2(g)
(i) Lead is
getting reduced.
(ii) Carbqn
dioxide is getting oxidised.
(iii) Carbon
is getting oxidised.
(iv) Lead
oxide is getting reduced.
(a) (i) and
(ii)
(b) (i) and
(iii)
(c) (i), (ii)
and (iii)
(d) all are
incorrect
Answer.
(a) (i) and
(ii)
Question 2.
Fe
2O
3 + 2Al ➝ Al
2O
3 + 2Fe
The above reaction is an
example of:
(a) combination reaction
(b) double
displacement,reaction
(c) decomposition reaction
(d) displacement reaction
Answer.
(d) displacement reaction
Question 3.
What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid
is added to iron filings? Tick the correct answer.
(a) Hydrogen
gas and iron chloride are produced.
(b) Chlorine
gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
(c) No
reaction takes place.
(d) Iron salt
and water are produced.
Answer.
(a) Hydrogen
gas and iron chloride are produced.
Question 4.
What is a balanced chemical equation? Why
should chemical equations be balanced? [2013]
Answer.
A chemical equation is said to be balanced
if:
(a) the atoms
of different elements on both sides of the equations are equal.
(b) the
equation is molecular, i.e. the gases if involved in the equation must be in
the molecular form (e.g. H
2, O
2, N
2, Cl
2, etc.).
Necessity to balance chemical
equations: The chemical equations have to be balanced to fulfil the
requirement of law of conservation of mass. According to the law, the total
mass of reactants
Question 5.
Transfer the following into chemical
equations and balance them:
(a) Hydrogen
gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
(b) Hydrogen
sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
(c) Barium
chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and
precipitate of barium sulphate.
(d) Potassium
metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Answer.
(a) The
symbol equation for the reaction is:
H
2 + N
2 ➝ NH
3
The balancing of equation is done in the
following steps:
Step I: Let
us count the number of atoms of all the elements of the reactants and the
products on both sides of the equation.
| Elements | No. of atoms of reactants (LHS) | No. of atoms of products (RHS) |
| H | 2 | 3 |
| N | 2 | 1 |
Step II: In
order to equate the number of H atoms on both sides, put coefficient 3 before
H
2 on the reactant side and coefficient 2 before NH
3 on the product side.
3H
2 + N
2 ➝ 2NH
3
Step III: On
counting, the number of N atoms on both sides of the equation are same. This
means that the equation is balanced.
Step IV: The
balanced equation can be written in physical state as:
3H
2(g) + N
2(g) ➝ 2NH
3(g)
(b) The
symbolic equation for the reaction is:
H
2S + O
2 ➝ H
2O + SO
2
The balancing of equation is done in the
following steps:
Step I: Let
us count the number of atoms of all the elements on both sides of the
equation.
| Elements | No. of atoms of reactants (LHS) | No. of atoms of products (RHS) |
| H | 2 | 2 |
| S | 1 | 1 |
| O | 2 | 3 |
Step II: In
order to equate the number of O atoms, put coefficient 3 before O2 on the
reactant side and coefficient 2 before SO2 on the product side.
H
2S + 3O
2 ➝ H
2O + 2SO
2
Step III: 0
atoms are still not balanced. To achieve this, put coefficient 2 before H
2O on the product side.
H
2S + 3O
2 ➝ 2H
2O + 2S0
2
Step IV: To
balance S atoms, put coefficient 2 before H
2S on the reactant side.
2H
2S + 3O
2 ➝ 2H
2O + 2SO
2
Step V: On
inspection, the number of atoms of all the elements on both sides of the
equation are equal. Therefore, the equation is balanced.
Step VI: The
balanced equation can be written in physical state as:
2H
2S(g) + 3O
2(g) ➝ 2H
2O(g) + 2SO
2(g)
(c) The
symbolic equatipn for the reaction is:
BaCl
2 + Al
2(SO
4)
3 ➝ AlCl
3 + BaSO
4
The balancing of equation is done in the
following steps:
Step I: Let
us count the number of atoms of all the elements on both sides of the
equation.
| Elements | No. of atoms of reactants (LHS) | No. of atoms of products (RHS) |
| Ba | 1 | 1 |
| Al | 2 | 1 |
| Cl | 2 | 3 |
| S | 3 | 1 |
| O | 12 | 4 |
Step II: In
order to equate the number of Al atoms, put coefficient 2 before AlCl3 on the
product side.
BaCl
2 + Al
2(SO
4)
3 ➝ 2AlCl
3 + BaSO
4
Step III: In
order to balance Cl atoms, put coefficient 3 before BaCl
2 on the reactant side.
3BaCl
2 + Al
2(SO
4)
3 ➝ 2AlCl
3 + BaSO
4
Step IV: To
balance Ba atoms, put coefficient 3 before BaSO
4 on the product side.
3BaCl
2 + Al
2(SO
4)
3 ➝ 2AlCl
3 +3BaSO
4
Step V: On
inspection, the number of S and 0 atoms on both sides of the equation are also
found to be equal. Thus, the equation is in balanced form.
Step VI: The
balanced equation can be written in physical state as:
3BaCl
2(aq) + Al
2(SO
4)
3(aq) ➝ 2AlCl
3(aq) + 3BaSO
4(s)
(d) The
symbolic equation for the reaction is:
K +
H
2O ➝ KOH + H
2
The balancing of equation is done in the
following steps:
Step I: Let
us count the number of atoms of all the elements on both sides.
| Elements | No. of atoms of reactants (LHS) | No. of atoms of products (RHS) |
| K | 1 | 1 |
| H | 2 | 3 |
| O | 1 | 1 |
Step II: To
balance the number of H atoms, put coefficient 2 before KOH on the product
side and 2 before H
2O on the reactant side.
K + 2H
2O ➝ 2KOH + H
2
Step III: To
balance the number of K atoms in the above equation, put coefficient 2 before
K atom on the reactant side.
2K + 2H
2O ➝ 2KOH + H
2
Step IV: On
inspection, the number of atoms of all the elements are found to be equal on
both sides of the equation. It is finally balanced.
Step V: The
balanced equation can be written in physical state as:
2K(s) + 2H
2O(l) ➝ 2KOH(aq) + H
2(g)
Question 6.
Balance the following chemical equations:
(a) HNO
3 + Ca(OH)
2 ➝ Ca(NO
3)
2 + H
2O
(b) NaOH + H
2SO
4 ➝ Na
2SO
4 + H
2O
(c) NaCl +
AgNO
3 ➝ AgCl + NaNO
3
(d) BaCl
2 + H
2SO
4 ➝ BaSO
4 + HCl
Answer.
(a) 2HNO
3 + Ca(OH)
2 ➝ Ca(NO
3)
2 + 2H
2O
(b) 2NaOH + H
2SO
4 ➝ Na
2SO
4 + 2H
2O
(c) The
symbolic equation as given for the reaction is already balanced.
NaCl + AgNO
3 ➝ AgCl + NaNO
3
(d) BaCl
2 + H
2SO
4 ➝ BaSO
4 + 2HCl
Question 7.
Write the balanced equations for the
following reactions:
(a) Calcium
hydroxide + Carbon dioxide ➝ Calcium carbonate + Water
(b) Aluminium
+ Copper chloride ➝ Aluminium chloride + Copper
(c) Barium
chloride + Potassium sulphate ➝ Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride
(d) Zinc +
Silver nitrate ➝ Zinc nitrate + Silver
Answer.
All these equations are in word form
whereas the balanced equations are written in symbolic form.
(a) Ca(OH)
2 + CO
2 ➝ CaCO
3 + H
2O
(b) 2Al +
3CuCl
2 ➝ 2AlCl
3 + 3Cu
(c) BaCl
2 + K
2SO
4 ➝ BaSO
4 + 2KCl
(d) Zn +
2AgNO
3 ➝ Zn(N0
3)
2 + 2Ag
Question 8.
Write the balanced chemical equations for
the following reactions and identify the type of reaction:
(a) Potassium
bromide(aq) + Barium iodide(aq) ➝ Potassium iodide(aq) + Barium bromide(aq)
(b) Zinc
carbonate(s) ➝ Zinc oxide(s) + Carbon dioxide (g)
(c) Hydrogen(g) + Chlorine (g) ➝ Hydrogen chloride (g)
(d) Magnesium(s) + Hydrochloric acid(aq) ➝ Magnesium chloride(aq) +
Hydrogen(g)
Answer.
(a) 2KBr(aq)
+ BaI
2(aq) ➝ 2KI(aq) + BaBr
2(aq)
The reaction is known as double
dis-placement reaction.
(b) ZnCO
3(s) ➝ ZnO(s) + CO
2(g)
The reaction is known as decomposition
reaction.
(c) H
2(g) + Cl
2(g) ➝ 2HCl (g)
The reaction is known as
combination reaction.
(d) Mg(s) +
2HCl(aq) ➝ MgCl
2(aq) + H
2(g)
The reaction is known as displacement
reaction.
Question 9.
What does one mean by exothermic and
endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Answer.
A chemical reaction in which certain amount
of heat energy is evolved and resulting contents get heated up is called
exothermic reaction.
Examples
2H
2(g) + O
2(g) ➝ 2H
2O(l) + heat
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) ➝ NaCl(aq)
+ H
2O(l) + heat
A chemical reaction is said to
be endothermic when certain amount of heat energy is absorbed.
Examples
N
2(g) + 0
2(g) + heat ➝ 2NO
C(s) + H
2O(g) + heat ➝ CO(g) + H
2(g)
Question 10.
Why is respiration considered an exothermic
reaction?
Answer.
Respiration is a biochemical reaction which
releases energy during combustion of digested food (glucose) in the cell
producing carbon dioxide and water.
C
6H
12O
6(S) + 6O
2(g) ➝ 6CO
2(g) + 6H
2O(l) + ATP
Question 11.
Why are decomposition reactions called the
opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer.
Decomposition reactions are called the
opposite of combination reactions because of the following:
- In decomposition reactions, larger molecules break to give simple molecules while in combination reactions, two or more smaller
- elements dr compounds combine to form new compounds.
- Decomposition reactions are endothermic while most of the combination reactions are exothermic. For example,
Combination reaction

Decomposition reaction
CaCO
3(s) ➝ CaO(s) + CO
2(g)
2Pb(NO
3)
2(s) ➝ 2PbO(s) + 4NO
2(g) + O
2(g)
Question 12.
Write one equation each for decomposition
reaction where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light and electricity.
Answer.

Question 13.
What is the difference between displacement
and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions. [2011]
Answer.
In a displacement reaction, one element
takes the place of another in a compound. For example,
Fe(s) + CuSO
4(aq) ➝ FeSO
4(aq) + Cu(s)
In a double displacement
reaction, one com-ponent each of both the reactants get exchanged to form the
products. For example,
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) ➝
NaCl(aq) + H
2O(l)
Question 14.
In the refining of silver, the recovery of
silver from silver nitrafe solution involved displacement by copper metal.
Write down the reactions involved.
Answer.
The chemical equation for the displacement
reaction is:

Question 15.
What do you mean by precipitation reaction?
Explain giving examples.
Answer.
In a precipitation reaction, one of the
products formed during the reaction does not dissolve in solution and gets
settled on the surface of the container (beaker or tube). It is known as a
precipitate.
Examples

Question 16.
Explain the following in terms of gain or
loss of oxygen with two examples of each:
(a) oxidation
(b) reduction
Answer.
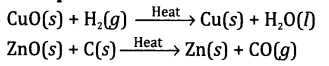
(a) Oxidation
involves the gain of oxygen by a substance in a chemical reaction.
Examples

(b) Reduction
involves the loss of oxygen from a substance in a chemical reaction.
Examples
Question 17.
A shining brown-coloured element ‘X’ on
heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element ‘X’ and the
black-coloured compound formed. [2013]
Answer.
The element ‘X’ is copper and the black-
coloured compound formed is copper(II) oxide.

Question 18.
Why do you apply paint on iron articles?
Answer.
Iron is a reactive metal. In the presence
of humid air (O
2 + H
2O), it rusts to form a layer of Fe
2O
3.xH
2O.
To prevent it from rusting, paint is
applied which forms a protective layer over iron and prevents direct contact
of air and water.
Question 19.
Oil and fat containing food items are
flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Answer.
Oil and fat containing food items or
eatables get rancid due to oxidation by air or oxygen. In case the container
or bag is flushed with nitrogen, then oxidation or rancidity will be checked.
Question 20.
Explain the following terms with one
example of each.
(a) Corrosion
(b) Rusting
Answer.
(a) Corrosion
Ijt is a chemical process of decay of metal when they are exposed to moisture.
(b) Rusting
Corrosion of iron is called rusting. It is a slow oxidation reaction which
takes place in the presence of moisture.
