Question 1.
Why are some substances biodegradable and some non-biodegradable?
Answer.
Substances: The substances that are broken down by biological processes, such as
the action of bacteria and, other saprophytes into simpler harmless substances
in due course of time are called biodegradable substances. Domestic waste
products, urine and faecal matter, agricultural wastes, wood, paper, cloth,
etc. are examples of biodegradable substances.
Non-biodegradable Substances: The substances that are not broken down by biological processes, but are acted upon by physical processes like heat and pressure under the ambient conditions found in the environment are called non-biodegradable substances. Plastics, glass objects, polythene bags, pesticides, metals such as mercury and lead, radioactive wastes, etc. are non-biodegradable substances.
Question 2.
Give any two ways in which biodegradable
substances would affect the environment.
Answer.
- The biodegradable substances can readily decompose. However, it may give out foul smell during the decomposition process.
- Flies breeding on the biodegradable substances would spread diseases like cholera, malaria, etc.
Question 3.
Give any two ways in which
non-biodegradable substances would affect the environment.
Answer.
-
They increase the burden on the environment as they cannot decompose and
simply
accumulate, causing land and water pollution. - Pesticides and chemicals enter the food chains and cause biomagnification.
Question 4.
What are trophic levels? Give an example of
a food chain and state the different trophic levels in it.
Answer.
Trophic Levels: The various steps or levels in a food chain where the transfer of food
energy takes place are called trophic levels. Producers or autotrophs
constitute the first trophic level. Herbivores or primary consumers constitute
the second trophic level. Carnivores or secondary consumers constitute the
third trophic level. Top carnivores or tertiary consumers constitute the
fourth trophic level.
Food Chain: A
sequence of living organisms in which each organism feeds on the other,
resulting in the transfer of food energy is known as food chain, e.g.

Question 5.
What is the role of decomposers in the
ecosystem?
Answer.
- Decomposers break down complex organic molecules of dead remains and wastes into simple organic molecules which can be easily absorbed by the plants.
- Decomposers channelise the raw materials and return it back to the environment. So, they maintain the nutrient pool of nature.
- They act as cleansing agent? of environment.
Question 6.
What is ozone and how does it affect any
ecosystem?
Answer.
Ozone Depletion
- Ozone is a molecule formed by three oxygen atoms.
- It is a deadly poison.
- At higher levels of the atmosphere, it forms an ozone layer which protects the earth’s surface from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiations from the sun.
-
The UV radiation splits molecular oxygen (02) into free oxygen atoms which
combine with molecular oxygen to form a molecule of ozone
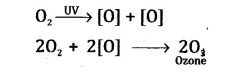
- Some ozone depleting substances like chloro- fluorocarbons react with ozone present in the stratosphere and depletie the ozone layer which causes global wanning.
Harmful Effects of Ozone Depletion
- Skin cancer
- Cataract
- Weakening of the immune system
- Decrease in reproductive capacity
- Inhibition of photosynthesis
Question 7.
How can you help in reducing the problem of
waste disposal? Give any two methods.
Answer.
- By maximising the use of articles which can be reused.
- By segregating the wastes before disposing. This will help us to identify the recyclable items.
Chapter End Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following groups contain only
biodegradable items?
(a) Grass,
flowers and leather
(b) Grass,
wood and plastic
(c) Fruit
peels, cake and lime juice
(d) Cake,
wood and grass
Answer.
(c) Fruit
peels, cake and lime juice
Question 2.
Which of the following constitute a food
chain?
(a) Grass,
wheat and mango
(b) Grass,
goat and human
(c) Goat, cow
and elephant
(d) Grass,
fish and goat
Answer.
(b) Grass,
goat and human
Question 3.
Which of the following are environment-
friendly practices?
(a) Carrying
cloth bags to put purchases in while shopping
(b) Switching
off unnecessary lights and fans
(c) Walking
to school instead of getting your mother to drop you on her scooter
(d) All of
the above
Answer.
(d) All of
the above
Question 4.
What will happen if we kill all the
organisms in one trophic level?
Answer.
If all the organisms of a trophic level are
killed, then the number of organisms of the lower trophic level would increase
tremendously. As a result of which, they would exhaust their food resources
too quickly and themselves starve to death. The organisms of the next higher
trophic level would die too because of non-availability of their food. Thus,
if one trophic level is disturbed, then the entire food chain gets affected.
Question 5.
Will the impact of removing all the
organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels? Can
the organisms of any trophic level be removed without causing any damage to
the ecosystem?
Answer.
Yes, the impact of removing all the
organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels. For
example, if in a forest ecosystem, all the carnivores, like lions, at the
third trophic level are removed, the number of herbivores in the second
trophic level would go on increasing. The herbivores would eat up all the
plants and turn the area into desert If all the herbivores are removed, then
the vegetation would go on increasing and the carnivores feeding on them would
die of starvation or migrate to other places. No, the organisms of any trophic
level cannot be removed without causing any damage to the ecosystem.
Question 6.
What is biological magnification? Will the
levels of this magnification be different at different levels of the
ecosystem?
Answer.
Biomagnification: The phenomenon that involves progressive accumulation of
non-biodegradable chemicals at each trophic level is called bio-magnification
or bio-accumulation. The maximum concentration of non-biodegradable chemicals
gets accumulated in the body of human beings.
The level of biological magnification would not be same at each level. It will go on increasing as . we move to higher trophic levels.
Question 7.
What are the problems caused by the non-
biodegradable wastes that we generate?
Answer.
- The biodegradable substances can readily decompose. However, it may give out foul smell during the decomposition process.
- Flies breeding on the biodegradable sub- ‘ stances would spread diseases like cholera, malaria, etc.
Question 8.
If all the waste we generate is
biodegradable, will this have no impact on the environment?
Answer.
Abundance of biodegradable waste encourages
bacterial growth. These bacteria when break down the waste, several foul
smelling gases are evolved, due to which the air gets polluted. If the
biodegradable waste gets piled into water bodies, the bacteria decomposing
them will soon depletes the available oxygen supplies leading to the death of
all aerobic life forms including itself. The only organisms able to survive
are anaerobic bacteria.
Question 9.
Why is damage to the ozone layer a cause
for concern? What steps are being taken to limit this damage?
Answer.
Ozone layer is like a protective shield for
the earth. It wards off harmful ultraviolet radiations coming from the sun.
Damage to this layer can result in increased level of ultraviolet radiations
filtering into our atmosphere. This would prove to be dangerous for all life
forms.
In 1987, UNEP succeeded in bringing 24 countries together to sign a contract. It is known as the famous ‘Montreal Protocol’. The Montreal Protocol highlighted the substances that cause depletion of the ozone Layer. The protocol asked the nations to limit the use of CFCs, halons and other man-made Ozone Depleting Chemicals (ODCs). It also asked the nations to look for alternate technology to replace CFCs.